Sentiment analysis in Trading is the talk of the town. In trading, sentiment analsysis plays a crucial role in understanding the market sentiment towards specific stocks, commodities, or currencies. It provides valuable insights into how traders and investors feel about certain assets, which can influence their decision-making process.
Sentiment analysis is analysing and interpreting emotions, opinions, and attitudes expressed in text data. Market sentiment refers to market participants’ overall attitude and emotions towards a particular financial instrument or market. It can influence the buying and selling decisions of traders and investors.
Sentiment analysis utilises natural language processing and machine learning techniques to determine the sentiment behind text data, whether positive, negative, or neutral.
The fundamentals of sentiment analysis involve analysing the text through various techniques such as keyword-based analysis, rule-based linguistic analysis, and machine learning-based analysis.
The steps to trading with sentiment analysis involve collecting relevant text data, preprocessing the data, performing sentiment analysis, and integrating the sentiment analysis results into trading strategies. Traders can use sentiment analysis to gauge market sentiment, identify trends, and make informed trading decisions.
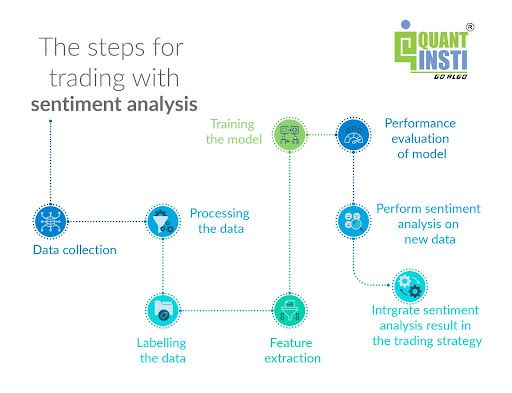
The steps include collecting and processing large amounts of text data from various sources, such as news articles, social media posts, and financial reports. It then applies algorithms and models to classify the sentiment expressed in the text.
The future of sentiment analysis in trading looks promising. As technology continues to advance, sentiment analysis techniques are expected to become more sophisticated, accurate, and integrated into trading platforms. This can lead to enhanced decision-making capabilities and improved trading performance for investors and traders.
All the concepts covered in this blog are taken from the Quantra course on Trading strategies with News and Tweets. You can take a Free Preview of the course and enrol to learn all these concepts in detail.
This blog covers the following topics in detail:
- What is market sentiment?
- Types of market sentiments
- What is sentiment analysis?
- Fundamentals of sentiment analysis
- Role of sentiment analysis in trading
- Sentiment indicators
- Sentiment trading strategies
- Sentiment analysis for trading
- Sentiment analysis for trading with Python
- Future of sentiment analysis in trading
Going forward, let us head to the introduction of market sentiment and sentiment analysis in detail. There are two important terms here: market sentiment and sentiment analysis. In simple words, sentiment analysis is driven by market sentiment.
But what does each term mean? Let us discuss below.
What is market sentiment?
The market sentiment reflects the collective psychology and view of market participants, which can influence their buying and selling decisions.
Various factors, including economic indicators, corporate earnings reports, geopolitical events, central bank policies, news sentiment, and social media sentiment influence market sentiment. It can significantly impact market dynamics, leading to price volatility, trends, and market cycles.
Traders and investors often monitor market sentiment to gain insights into market behaviour and make informed trading decisions. They may use sentiment analysis techniques, such as analysing news sentiment, social media sentiment, or survey data, to gauge the prevailing sentiment and sentiment shifts in the market.
Types of Market Sentiments
Market sentiment can be categorised into three main types:
Bullish Sentiment
Bullish sentiment occurs when the majority of market participants have a positive outlook on the market or a specific asset. They expect prices to rise and may be more inclined to buy and hold assets in anticipation of future gains. Positive economic news, favourable market conditions, and strong investor confidence can contribute to bullish sentiment.
Bearish Sentiment
Bearish sentiment, on the other hand, represents a negative outlook on the market or a specific asset. Market participants with bearish sentiment expect prices to decline and may take actions such as selling assets or short-selling in anticipation of future losses. Negative economic news, geopolitical uncertainties, and pessimistic investor sentiment can contribute to bearish sentiment.
Neutral Sentiment
Neutral sentiment reflects a more balanced or indifferent attitude towards the market. Market participants with neutral sentiments may neither strongly believe in an upward nor downward price movement. They may adopt a wait-and-see approach, observing market developments before making any significant trading decisions.
It’s important to note that market sentiment is subjective and can change rapidly based on new information or events. Therefore, combining market sentiment analysis with other fundamental and technical analyses is crucial to form a comprehensive view of the market and make well-informed trading decisions.
What is sentiment analysis?
Sentiment analysis is the process of analysing and interpreting the emotions, opinions, and attitudes expressed in text data. It involves using natural language processing (Learn the natural language processing python course from Quantra) and machine learning techniques to determine the sentiment behind the text, whether positive, negative, or neutral.
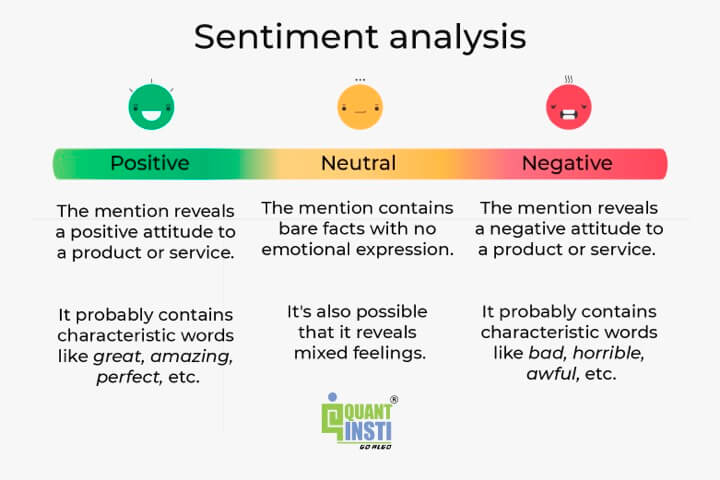
The goal of sentiment analysis is to understand the subjective information conveyed in text and extract meaningful insights from it. It has applications in various domains, including:
- social media analysis,
- customer feedback analysis,
- brand reputation management,
- market research, and
- financial trading.
Sentiment analysis provides valuable insights into public opinion, customer sentiment, or market sentiment. It helps businesses to:
- understand customer feedback,
- identify trends,
- measure brand reputation, and
- make data-driven decisions.
In financial trading, sentiment analysis can be used to:
- gauge market sentiment,
- identify potential risks or opportunities, and
- inform trading strategies.
It’s important to note that sentiment analysis is not perfect and can be challenging due to the complexity of language, sarcasm, irony, and context. Therefore, it’s crucial to continuously refine and improve the sentiment analysis models based on feedback and domain-specific requirements.
Fundamentals of sentiment analysis
The fundamentals of sentiment analysis involve understanding the key concepts and techniques used in analysing and interpreting sentiment in text data. Here are the fundamental aspects of sentiment analysis:
Text preprocessing
Preprocessing text data is an essential step in sentiment analysis. It involves cleaning the text by removing noise, such as special characters, punctuation, and HTML tags. Additionally, converting the text to lowercase, removing stopwords (common words with little semantic meaning), and performing tokenisation (splitting text into individual words or tokens) are commonly applied preprocessing techniques.
Sentiment lexicons
Sentiment lexicons are dictionaries or databases that associate words with sentiment scores or labels. They contain a list of words and their corresponding polarity, indicating whether they are positive, negative, or neutral. Lexicons serve as a valuable resource for sentiment analysis, as they help assign sentiment labels to words in the text.
Rule-based approaches
Rule-based approaches rely on predefined linguistic rules to determine the sentiment of a text. These rules can be based on grammatical patterns, syntactic structures, or a combination of word-level and context-based rules. Rule-based approaches are often used in conjunction with sentiment lexicons to classify sentiment.
Machine learning approaches
Machine learning techniques are widely used in sentiment analysis. Supervised learning algorithms, such as Naive Bayes, Support Vector Machines (SVM), and Random Forests, are commonly applied. These algorithms are trained on labelled datasets, where the sentiment of the text is known, and then used to predict the sentiment of unseen text data.
Feature extraction
Feature extraction involves converting the preprocessed text data into numerical features that can be used as input for sentiment analysis models. Common feature extraction techniques include the bag-of-words model, which represents the text as a frequency distribution of individual words or n-grams, and TF-IDF (Term Frequency-Inverse Document Frequency), which weights words based on their importance in a specific document relative to a collection of documents.
Neural Networks and Deep Learning
Deep learning models, particularly neural networks, have shown significant advancements in sentiment analysis. Recurrent Neural Networks (RNN), such as Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) and Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU), are widely used for sequence modelling and sentiment analysis tasks. These models can capture contextual dependencies and long-term dependencies in text data.
Evaluation metrics
Various evaluation metrics are used to assess the performance of sentiment analysis models. Common metrics include accuracy, precision, recall, and confusion matrix. These metrics help measure the model’s ability to classify sentiment and determine its overall effectiveness correctly.
It’s important to note that continuous experimentation and refinement are necessary to improve the accuracy and effectiveness of sentiment analysis models.
Stay tuned for the next installment to learn about sentiment analysis role in trading.
Originally posted on QuantInsti blog.
Disclosure: Interactive Brokers
Information posted on IBKR Campus that is provided by third-parties does NOT constitute a recommendation that you should contract for the services of that third party. Third-party participants who contribute to IBKR Campus are independent of Interactive Brokers and Interactive Brokers does not make any representations or warranties concerning the services offered, their past or future performance, or the accuracy of the information provided by the third party. Past performance is no guarantee of future results.
This material is from QuantInsti and is being posted with its permission. The views expressed in this material are solely those of the author and/or QuantInsti and Interactive Brokers is not endorsing or recommending any investment or trading discussed in the material. This material is not and should not be construed as an offer to buy or sell any security. It should not be construed as research or investment advice or a recommendation to buy, sell or hold any security or commodity. This material does not and is not intended to take into account the particular financial conditions, investment objectives or requirements of individual customers. Before acting on this material, you should consider whether it is suitable for your particular circumstances and, as necessary, seek professional advice.
Disclosure: Forex
There is a substantial risk of loss in foreign exchange trading. The settlement date of foreign exchange trades can vary due to time zone differences and bank holidays. When trading across foreign exchange markets, this may necessitate borrowing funds to settle foreign exchange trades. The interest rate on borrowed funds must be considered when computing the cost of trades across multiple markets.
Disclosure: Futures Trading
Futures are not suitable for all investors. The amount you may lose may be greater than your initial investment. Before trading futures, please read the CFTC Risk Disclosure. A copy and additional information are available at ibkr.com.














Join The Conversation
If you have a general question, it may already be covered in our FAQs. If you have an account-specific question or concern, please reach out to Client Services.