The article “What is Quantamental? 3 Techniques to Investing” first appeared on AlgoTrading101 blog.
What is Quantamental? Quantamental is a term that describes a hybrid of quantitative and fundamental techniques to investing.
This term is a fancy buzzword that is gaining popularity as it is a convenient marketing angle.
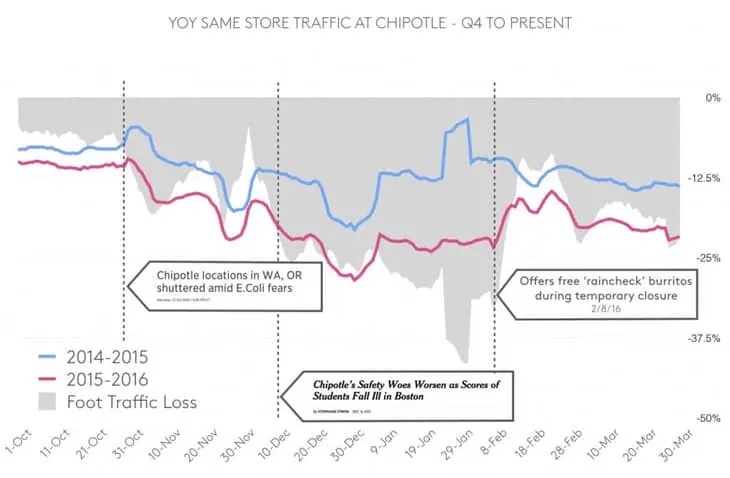
Foursquare predicts Chipotle earnings by analysing foot traffic around Chipotle stores. Credit: medium.com
Quantamental techniques have been around for a while. Most firms use a mix of quantitative and qualitative fundamental techniques.
Traditional hedge funds have been using quantitative techniques to supplement their qualitative analysis.
Quantitative funds largely use quantitative techniques (you don’t say!) but in certain strategies, they might still use some qualitative analysis to supplement the quantitative analysis. E.g. When the COVID-19 crisis happens, they might intervene in strategies that don’t work in volatile environments.
Let’s look at 3 categories of quantamental techniques in this article:
- Quantamental Techniques for an Individual Asset
- Quantamental Techniques for Event Trading
- Quantamental Techniques at a Portfolio level
We’ll cover both fundamental and quantitative methods in each category.
When we use both fundamental and quantitative methods appropriately in our research, that is our quantamental technique.
Quantamental Techniques for an Individual Asset
Case study 1: A stock
Fundamental Analysis
Traditional fundamental analysis methods include:
- Analysing the business fundamentals
- Estimating market size and future market growth
- Understanding the competence and commitment of the CEO and management team
- Making a prediction on how certain industries will evolve and how the stock will react to this evolution
- Making sure the CEO isn’t self-dealing, making money at the company’s expense and getting a billion dollar personal bailout as the company is forced to cut staff
Quantitative Analysis
Quantitative methods include:
- Sending out drone operators to count how many cars a factory produces
- Using foot traffic data from consumer apps to predict how many people went to a fast food restaurant
- Hiring surveyors to check how many plant-based meats are being sold at supermarkets
- Buying users web behaviour data (illegally?) from anti-virus software
- Scanning thousands of companies by their fundamental data (P/E ratios, book values etc) to select promising companies
- Reading thousands of annual reports using machine learning to extract sentiment
- Spending hundreds of millions to buying credit card expenditure data
- Predicting iPhone sales by analysing foot traffic around Apple stores
Apple @ One Stockton Street Place Shape from Foursquare on Vimeo.
Predicting iPhone sales by analysing foot traffic around Apple stores
I think most, if not all, traditional hedge fund managers would set up quantitative analytics teams to analyse those juicy data if they had access to them.
However, this is not a foolproof method to trade. Getting data with good predictive value is expensive. Valuable data are getting rarer. The value from these data decays as more players obtain them.
Case Study 2: A commodity – Oil
Fundamental Analysis
Traditional fundamental analysis methods include:
- Talking to oil brokers to understand the demand and supply dynamics
- Understand the political situation between big oil producing countries and their partners
- Lobbying the government?

Oil storage tanks. Credit: Planet.com
Quantitative Analysis
Quantitative methods include:
- Analysing satellite images of oil tank storage roofs
- Checking the traffic conditions in cities after the COVID-19 crisis to see if they are reopening their economy. More traffic = more oil required
- Evaluating aircraft fuel demand by web scraping flight schedules data off a flight scanning site
Quantamental Techniques for Event Trading
Next, we look at how to use quantamental techniques for event-driven trades. This means that we are betting on an outcome of an event.
Case study: Brexit
Brexit is the withdrawal of UK from the EU. I won’t spend time talking about what is Brexit, you can read more here.
Fundamental Analysis
Traditional fundamental analysis methods include:
- Listening to arguments by pro-brexit and anti-brexit politicians
- Understanding the dynamics between UK leaders and EU leaders
Quantitative Analysis
Quantitative methods include:
- Launching a mass poll to survey the people’s opinion on Brexit and making hundreds of millions!
I’m sure hedge funds are doing these mass polls to trade the upcoming 2020 presidential elections.
Quantamental Techniques at a Portfolio level
In a sense, portfolio design and optimisation has always been quantitative.
The Markowitz Portfolio Theory (AKA Modern Portfolio Theory AKA MPT) influenced the way fund managers have been building their portfolios since the 1950s.
MPT entails designing a group of assets in a way that maximises expected returns while minimising volatility.
Fundamental Analysis
Traditional fundamental analysis methods include:
- Markowitz Portfolio Theory
- Adjusting offense and defense based on where we are in market cycles
- Fama-French 3-factor model
- Carhart four-factor model
Quantitative Analysis
Quantitative methods include:
- Risk parity models (sometimes known as smart beta) – neutralising market, sector and other risks. Examples:
- Statistical arbitrage models – this is more of a trading model than an investing model. This involves buying stocks that dipped and shorting those that spiked while maintaining market neutrality.
End note
Even though quantitative methods are more recent than fundamental methods, they aren’t necessarily better. Fundamental methods aren’t necessarily better than quantitative methods either.
Both fundamental and quantitative methods have their advantages and disadvantages. It depends on how they are applied and the skills of the practitioner.
Disclosure: Interactive Brokers
Information posted on IBKR Campus that is provided by third-parties does NOT constitute a recommendation that you should contract for the services of that third party. Third-party participants who contribute to IBKR Campus are independent of Interactive Brokers and Interactive Brokers does not make any representations or warranties concerning the services offered, their past or future performance, or the accuracy of the information provided by the third party. Past performance is no guarantee of future results.
This material is from AlgoTrading101 and is being posted with its permission. The views expressed in this material are solely those of the author and/or AlgoTrading101 and Interactive Brokers is not endorsing or recommending any investment or trading discussed in the material. This material is not and should not be construed as an offer to buy or sell any security. It should not be construed as research or investment advice or a recommendation to buy, sell or hold any security or commodity. This material does not and is not intended to take into account the particular financial conditions, investment objectives or requirements of individual customers. Before acting on this material, you should consider whether it is suitable for your particular circumstances and, as necessary, seek professional advice.
Disclosure: Futures Trading
Futures are not suitable for all investors. The amount you may lose may be greater than your initial investment. Before trading futures, please read the CFTC Risk Disclosure. A copy and additional information are available at ibkr.com.














Join The Conversation
If you have a general question, it may already be covered in our FAQs. If you have an account-specific question or concern, please reach out to Client Services.